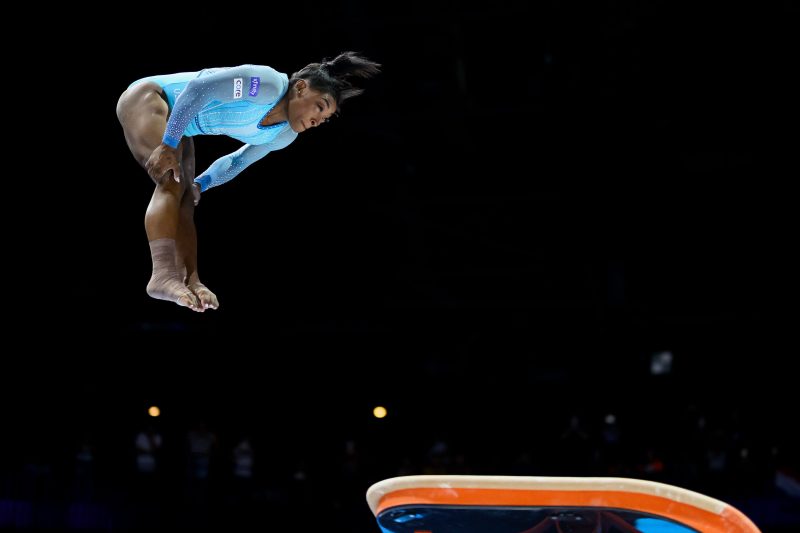Editor’s note: FollowOlympic opening ceremony live updates.
In addition to her record number of medals — she has 37 at the world championships and Olympics, more than any other gymnast, male or female — Biles has five skills named after her in the Code of Points, gymnastics’ scoring systems. Skills are named after the first gymnast to do them in a major international competition, like the world championships or Olympics. This means that long after Biles is done with gymnastics, her presence will remain.
How many gymnastics skills are named after Simone Biles?
Five total: Two on vault, two on floor exercise and one on balance beam. Here’s a closer look at each one.
Meet Team USA: See which athletes made the U.S. Olympic team and where they are from
The Biles I on floor exercise
What the move is: It’s a double layout with a half-twist, which means a double somersault in the stretched position, with a half-twist. Once considered one of the hardest passes to do, it’s now the third pass in her floor routine. In other words, she’s perfected it so well she can do it well into her floor routine, even after she’s already expended a lot of energy.
When Biles first did it: This was the first skill Biles had named after her, back in 2013.
Has anyone else done it? A handful of other gymnasts have since done this skill.
The Biles II on floor exercise
What the move is: It’s a triple-double, which means it’s a triple-twisting, double somersault. It’s now her first pass in her floor routine.
When Biles first did it: This was first done in 2019.
The Biles I on vault
What the move is: It’s a roundoff onto the takeoff board, a back handspring with a half-turn onto the table, followed by a double-twisting somersault in a stretched position.
When Biles first did it: When Biles had this named after her in 2018, it matched the Produnova for most difficult vault in the women’s code. But the Biles II has since surpassed them both, so she no longer does the Biles I on vault.
The Biles II on vault
What the move is: The Biles II is also known as the Yurchenko double pike. Vaults are categorized by “families,” which are based on the entry. On Yurchenko vaults, a gymnast does a roundoff onto the takeoff board and a back handspring onto the table. Biles then follows it with a double somersault in the piked position.
Has anyone else done it? Few men even try this vault, which is so difficult because of the power it takes to get two somersaults as well as its lack of a bailout. If something goes awry, more likely to land on her head or neck than her knees.
When Biles first did it: Biles began doing this vault in 2021 but didn’t do it at a worlds or Olympics until the 2023 world championships. With a 6.4 difficulty value, it is the hardest vault in the women’s code.
When Biles did the vault last year, she took a half-point deduction for having coach Laurent Landi standing on the landing mat, ready to step in and redirect her into a safe position if it looked as if she was headed for a scary landing. But neither Biles nor Landi feel the need for him to do that anymore.
The most difficult vault commonly executed by other gymnasts is valued at 5.6, eight-tenths lower than the Biles II, so doing it gives Biles a huge scoring advantage
The Biles on balance beam
What the move is: It’s the double-double dismount, which means it’s a double-twisting, double somersault.
When Biles first did it: She first did it in 2019. Biles no longer does this skill because it isn’t worth it score-wise.
Has anyone else done it? The international gymnastics federation (FIG) undervalued the dismount because it didn’t want to encourage less-competent gymnasts trying it. Which is silly. The whole point of an open-ended code is to push the boundaries of the sport. If the FIG was really that concerned, it would tell judges to use the execution mark to hammer gymnasts who try skills they have no business doing. One 10, when everyone else is scoring in the 14s, would have gotten the message across equally well.
How do you get a gymnastics move named after you?
Skills are named after the first gymnast to do them in a major international competition, like the world championships or Olympics.